Table of Contents
Nursing Care Plan for Acute Pain Management: Strategies and Interventions

The nurse care plan for acute pain management is a comprehensive guideline that outlines nursing strategies and interventions for assessing, diagnosing, planning, implementing, and evaluating effective pain management techniques for patients with acute pain. This approach seeks to give patients with tailored care and to ensure optimal pain relief while avoiding the negative effects and complications associated with pain management.
Definition Of Acute Pain
Acute pain is a type of pain that occurs unexpectedly and lasts for a short period of time, usually less than 3 to 6 months. It is frequently defined as a sudden, acute, and localized pain that alerts the body that something is wrong or injured. Various illnesses, such as surgery, trauma, infection, inflammation, or medical procedures can cause acute pain. It usually goes away once the underlying cause is treated or the tissue damage heals. Acute pain, on the other hand, can progress to chronic pain and other consequences if left untreated.
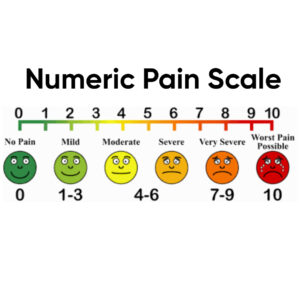
Before developing a care plan for acute pain, it is crucial to assess the patient’s pain intensity, location, and duration. The use of pain scales, such as the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS), can be helpful in assessing pain intensity. The pain assessment should also consider the patient’s medical history, current medications, and any comorbidities that may impact pain management.
The diagnosis of acute pain is usually based on the patient’s subjective reports of pain and the assessment findings. The diagnosis should be specific and include the underlying cause of the pain.
The planning and implementation of a care plan for acute pain should be based on the patient’s individual needs and preferences. The use of non-pharmacological interventions, such as relaxation techniques, distraction, and massage, can be effective in managing pain. Pharmacological interventions, such as analgesics, should be used as per the patient’s pain severity and medical condition.
The choice of analgesics should be guided by the World Health Organization (WHO) pain ladder, which recommends starting with non-opioid analgesics such as paracetamol or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for mild pain and escalating to opioid analgesics for moderate to severe pain.
NANDA Approved Nursing Diagnosis for Acute Pain
- Acute Pain related to tissue trauma or surgical intervention as evidenced by verbal reports of pain, facial grimacing, and increased heart rate
2. Ineffective coping related to pain experience as evidenced by statements of feeling overwhelmed or helpless and the inability to manage pain on their own.
3. Anxiety related to the perception of pain as evidenced by restlessness, agitation, and/or increased respiratory rate
4. Risk for falls related to pain as evidenced by unsteady gait or reluctance to move
Acute Pain related to tissue trauma or surgical intervention as evidenced by verbal reports of pain, facial grimacing, and increased heart rate
Assessment:
- Assess the location, intensity, and quality of the pain, and ask the patient to describe the pain
- Determine the onset, duration, and frequency of the pain
- Assess the patient’s level of anxiety and coping mechanisms
- Monitor vital signs including heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate
- Observe for signs of discomfort such as facial grimacing, guarding, and restlessness
Goal:
The patient’s pain will be effectively managed to improve comfort and overall well-being.
Nursing Interventions & Rationales:
- Administer pain medications as ordered by the physician, including both opioid and non-opioid analgesics.
Pain medications provide relief from pain and improve the patient’s overall comfort.
- Provide non-pharmacologic pain management techniques such as distraction, relaxation techniques, and guided imagery.
Non-pharmacological pain management techniques can be used in conjunction with medications to reduce pain and anxiety.
- Encourage the patient to report pain promptly to allow for timely intervention.
Prompt reporting of pain allows for timely intervention and improved management of pain.
- Educate the patient about the medication’s potential side effects and how to manage them.
Education about medication side effects and management allows the patient to be informed and proactive in their pain management.
- Position the patient comfortably and assist with repositioning to minimize discomfort.
Comfortable positioning and repositioning can minimize discomfort and improve comfort.
- Provide wound care and other interventions to manage pain related to the surgical incision or other traumatic injuries.
Wound care and other interventions can help manage pain related to the underlying injury or condition.
- Monitor vital signs and pain levels regularly to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions and to adjust the care plan as needed.
Regular monitoring of vital signs and pain levels is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions and modifying the care plan as needed.
Evaluation:
- Monitor the patient’s pain level and vital signs regularly to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
- Document the patient’s response to interventions and adjust the care plan as necessary.
- The patient reports a decrease in pain level and increased comfort.
- The patient demonstrates an understanding of medication side effects and management.
- The patient is able to participate in activities of daily living with minimal discomfort.
Ineffective coping related to pain experience is evidenced by statements of feeling overwhelmed or helpless and the inability to manage pain on their own.
Assessment:
- Assess the patient’s ability to cope with pain and their understanding of pain management techniques.
- Assess the patient’s emotional state and level of anxiety.
- Identify any additional stressors or life events that may be contributing to the patient’s difficulty in coping with pain.
- Assess the patient’s support system, including family and friends.
- Determine the patient’s previous experience with pain and pain management.
Goal:
The patient will effectively manage their pain and demonstrate improved coping skills.
Nursing Interventions & Rationales:
- Assess and validate the patient’s feelings of helplessness and provide emotional support.
Validating the patient’s feelings of helplessness and providing emotional support can help to reduce anxiety and promote a sense of control.
- Teach the patient pain management techniques such as deep breathing, relaxation techniques, guided imagery, and distraction techniques.
Pain management techniques can be used in conjunction with medication to reduce pain and promote relaxation.
- Encourage the patient to express their feelings and fears related to pain.
Encouraging the patient to express their feelings and fears related to pain can promote emotional healing.
- Assist the patient in identifying and utilizing available resources such as support groups or counseling services.
Identifying and utilizing available resources can provide additional support to the patient.
- Provide information about medication options and potential side effects, and encourage the patient to report any adverse effects.
Educating the patient about medication options and potential side effects can empower them to make informed decisions about their pain management.
- Provide opportunities for the patient to participate in decision-making related to their pain management.
Encouraging the patient to participate in decision-making related to their pain management promotes a sense of control.
- Work with the patient to identify coping strategies that have been effective for them in the past.
Identifying coping strategies that have been effective for the patient in the past can promote a sense of self-efficacy.
- Provide positive feedback and reinforcement to the patient for utilizing effective coping strategies.
Evaluation:
- Monitor the patient’s pain level and assess their ability to effectively manage pain.
- Monitor the patient’s emotional state and level of anxiety.
- Document the patient’s response to interventions and adjust the care plan as necessary.
- The patient reports feeling more in control of their pain and emotions.
- The patient is able to effectively utilize pain management techniques.
- The patient is able to identify and utilize available resources.
- The patient demonstrates improved coping skills and a sense of self-efficacy.
Anxiety related to the perception of pain as evidenced by restlessness, agitation, and/or increased respiratory rate
Assessment:
- The patient displays restlessness, agitation, and/or increased respiratory rate.
- The patient reports anxiety related to the perception of pain.
Goal:
The patient will report a reduction in anxiety related to pain perception.
Nursing Interventions & Rationales
Assess the patient’s pain level and anxiety level regularly and document findings.
Rationale: Regular assessments of pain and anxiety levels can provide useful information for planning care and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions.
Administer prescribed pain medication as ordered.
Rationale: Pain medication can alleviate the physical symptoms of pain, which can reduce the patient’s anxiety levels.
Encourage the patient to use relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises and visualization.
Rationale: Relaxation techniques can reduce muscle tension and promote a sense of calm, which can help to alleviate anxiety.
Provide a quiet and calm environment for the patient.
Rationale: A quiet and calm environment can help to reduce the patient’s anxiety levels.
Encourage the patient to verbalize their feelings and concerns related to pain and anxiety.
Rationale: Verbalizing feelings and concerns can help the patient to process and manage their emotions related to pain and anxiety.
Evaluation:
The patient reports a reduction in anxiety related to pain perception.
Vital signs indicate a decreased respiratory rate and an improved level of restlessness and agitation.
Risk for falls related to pain as evidenced by unsteady gait or reluctance to move.
Assessment:
- The patient displays an unsteady gait or reluctance to move due to pain.
- The patient has a history of falls or risk factors for falls, such as age or cognitive impairment.
Goal:
The patient will remain free from falls during hospitalization.
Nursing Interventions & Rationales
Assess the patient’s gait and mobility regularly and document findings.
Rationale: Regular assessments of gait and mobility can provide useful information for planning care and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions.
Encourage the patient to use assistive devices such as a walker or cane when ambulating.
Rationale: Assistive devices can improve the patient’s stability and reduce the risk of falls.
Ensure that the patient’s room is free of clutter and hazards.
Rationale: A clear and safe environment can reduce the risk of falls.
Educate the patient on the importance of calling for assistance when getting out of bed or moving around.
Rationale: Calling for assistance can reduce the risk of falls by ensuring that the patient has support and assistance when needed.
Administer pain medication as ordered to reduce pain and improve mobility.
Rationale: Pain medication can alleviate the physical symptoms of pain, which can improve the patient’s mobility and reduce the risk of falls.
Evaluation:
- The patient remains free from falls during hospitalization.
- The patient reports improved mobility and ability to move without pain.
Follow-up & Evaluation of Acute Pain Nursing Care Plan
The evaluation and follow-up of a care plan for acute pain are critical to ensure its effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments. The patient’s pain intensity should be assessed regularly using pain scales, and the care plan should be modified accordingly. The use of patient education and counseling can also be effective in improving pain management outcomes.
You May Also Like
Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension
Nursing Care Plan for Postpartum Hemorrhage