The immune system is a complex network of cells and proteins that defends the body against infection. The immune system keeps a record of every germ (microbe) it has ever defeated so it can recognize and destroy the microbe quickly if it enters the body again.
Table of Contents
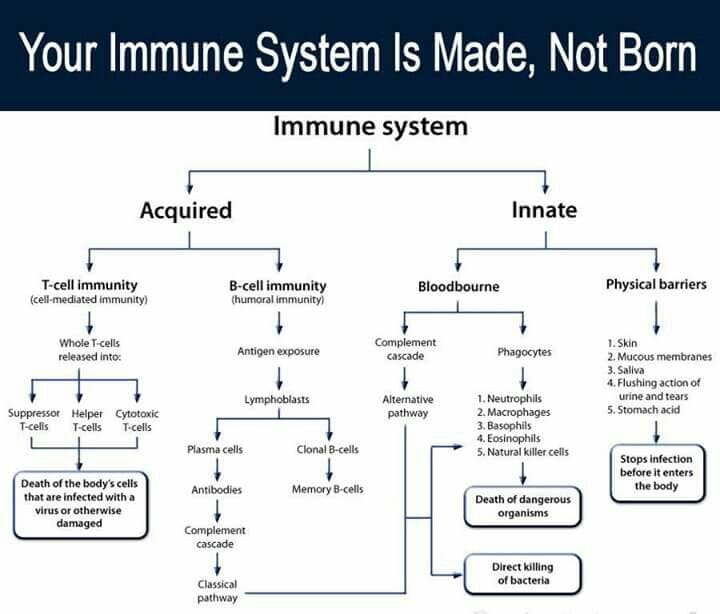
Types of Immune Response
- Nonspecific Immune Response
- Specific Immune Response
Nonspecific Immune Response
It is directed against invading microbes. The examples of nonspecific immune response includes Physical barriers and bloodbourne nonspecific immune response
Physical Barriers includes
1.Body surface barriers: intact skin and mucosa, cilia, and mucus secretions
2. Antimicrobial secretions: oil of skin, tears, gastric juice, and vaginal secretions
Bloodbourne Nonspecific Immune Response includes
1. Internal antimicrobial agents
a. Interferon: It is a substance produced within cells in response to viral attack
b. Properdin (Factor P): It is a protein agent in blood that destroys certain gram-negative bacteria and viruses
c. Lysozyme: destroys mainly gram-positive bacteria
2. Phagocytes (monocytes, macrophages, Natural Killer Cells, Dendritic cells): cells that ingest and destroy microbes; part of the reticuloendothelial system
3. Inflammatory response
First stage: the release of histamine and chemical mediators (e.g., prostaglandin, bradykinin) leads to vascular dilation and increased capillary permeability, resulting in signs of inflammation (e.g., pain, heat, redness, edema, and loss of function)
Second stage: exudate production
Third stage: reparative phase
Specific immune response
It directed against a specific pathogen (foreign protein) or its toxin; may be cell-mediated or humoral
Cell-mediated immunity (T-cell immunity)
- Occurs within cells of the immune system
- Involves T lymphocytes (e.g., T helper, T suppressor, T cytotoxic, lymphokines); each type plays a distinct role in immune response
- Cluster designations: mature T cells carry markers on the surface that permit them to be classified structurally (e.g., CD4 cells associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome [AIDS])
Functions of cell-mediated immunity
- Protect against most viral, fungal, protozoan, and slow-growing bacterial infections
- Reject histoincompatible grafts
- It causes skin hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., tuberculosis [TB] screening)
- Assists with diagnosis of malignancies
Humoral immunity (B-cell Immunity)
- It concerned with immune responses outside of cell
- It involves B lymphocytes that differentiate into plasma cells and secrete antibodies
Antibody:
- Immune substance produced by plasma cells;
- Antibodies are gamma globulin molecules;
- Antibodies are commonly referred to as immunoglobulin (Ig)
Antigen:
Any substance, including allergen, that stimulates the production of antibodies in the body
Typically, antigens are foreign proteins, most potent being microbial cells and their products
Complement-fixation:
- Complement is a group of blood serum proteins needed in certain antigen-antibody reactions;
- Both complement and antibody must be present for the reaction to occur
Immunoglobulins (Antibodies)
There are five types of immunoglobulins in our body. They are:-
- IgM
- IgG
- IgA
- IgE
- IgD
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies:
It is a first antibodies to be detected after exposure to antigen; protection from gram-negative bacteria
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies:
- It makes up more than 75% of total immunoglobulins;
- The highest increase in response to subsequent exposure to antigen;
- The only immunoglobulin that passes the placental barrier
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies
- It responsible for hypersensitivity and allergic responses;
- It causes mast cells to release histamine;
- It helps to protect from parasites
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies
It present in blood, mucus, and human milk secretions; play important role against viral and respiratory pathogens
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) antibodies
It helps to differentiate B lymphocytes
Types of Humoral Immunity
Mainly Two Types
- Active Immunity
- Passive Immunity
Active Immunity
It means antibodies formed in body.
It is two types
- Natural Active Immunity
- Artificial Active Immunity
Natural active immunity
It means antibodies formed during course of disease; may provide lifelong immunity (e.g., measles, chickenpox, yellow fever, smallpox
Artificial active immunity
The vaccine or toxoid stimulate formation of homologous antibodies; revaccination (booster shot) often needed to sustain antibody titer (anamnestic effect)
Artificial Active Immunity Produced by Administration of:-
a. Live vaccines: antigenic preparations containing weakened (attenuated) microbes; typically such vaccines are more antigenic than killed preparations (e.g., oral [Sabin] poliomyelitis vaccine, measles vaccine)
b. Killed vaccines: antigenic preparations containing killed microbes (e.g.,pertussis vaccine, typhoid vaccine)
c. Toxoids: antigenic preparations composed of inactivated bacterial toxins (e.g., tetanus toxoids, diphtheria toxoids)
Passive immunity
Antibodies acquired from outside source produce short-term immunity
It is also two types;
- Natural Passive Immunity
- Artificial Passive Immunity
Natural passive immunity
- It is the passage of preformed antibodies from mother through the placenta to fetus or through the colostrum to neonate;
- During the first few weeks of life, the newborn is immune to certain diseases to which the mother has active immunity
Artificial passive immunity
- It is acquired by injection of antisera derived from immunized animals or humans;
- It provides immediate protection and also is of value in treatment (e.g., diphtheria antitoxin, tetanus antitoxin)
Nursing Exams Important Points to Remember
Please Subscribe Our YouTube channel – The Nurse
Like our Facebook Page: The Nurse
Please Subscribe to get all our posts in your mail inbox