Boggy uterus is a condition that affects women during and after childbirth. It is a potentially dangerous condition that can lead to postpartum hemorrhage and other serious complications.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for a boggy uterus is essential for women who may be at risk, as well as for their healthcare providers.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about a boggy uterus, including how it differs from other uterine conditions, how it can be prevented, and strategies for coping with its physical and emotional effects.
Table of Contents
Understanding Boggy Uterus: Causes and Symptoms
What is Boggy Uterus?
If you’ve just given birth, you may have come across the term “boggy uterus“. Simply put, a boggy uterus refers to a uterus that feels soft and flaccid instead of firm and contracted. It’s a common condition that occurs after childbirth and can be a sign of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH).
Causes of Boggy Uterus
The most common cause of a boggy uterus is uterine atony, which means the uterus fails to contract after delivery. This can lead to heavy bleeding and put the mother at risk of PPH. Other factors that can contribute to a boggy uterus are multiple births, prolonged labor, and the use of medications to induce or speed up labor.
Symptoms of Boggy Uterus
The symptoms of a boggy uterus may vary, but some common signs to look out for are excessive bleeding, a uterus that feels soft and enlarged, and an inability to pass urine. If left untreated, a boggy uterus can lead to severe complications, making prompt medical attention necessary.
Risks and Complications Associated with Boggy Uterus
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is a severe complication that can occur due to a boggy uterus. It can lead to excessive bleeding, shock, and even death if not treated promptly. Therefore, it’s essential to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any symptoms of a boggy uterus.
Loss and Anemia
Excessive blood loss due to a boggy uterus can lead to anemia, a condition where your body lacks sufficient red blood cells. Anemia can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath, making it difficult to take care of your newborn.
Uterine Infection
A boggy uterus can also increase your risk of developing a uterine infection, especially if you have a C-section or prolonged labor. Symptoms of a uterine infection include fever, chills, and abdominal pain.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Boggy Uterus
Medical Evaluation and Diagnosis
If you experience any symptoms of a boggy uterus, your healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination to determine the cause of your symptoms. They may also order blood tests to check your hemoglobin levels and coagulation factors.
Treatment Options for Boggy Uterus
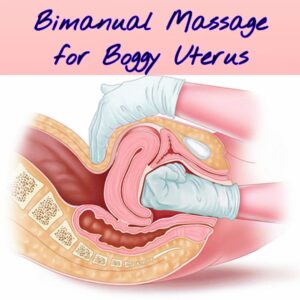
The treatment for a boggy uterus depends on the severity of your symptoms. If you have a mild case, your healthcare provider may massage your uterus to help it contract. If your symptoms are severe, you may need medications such as oxytocin or misoprostol to stimulate uterine contractions.
Medications and Surgery
In some cases, you may need surgery to remove any remaining tissue or blood clots from your uterus. If medication and other treatments fail to stop the bleeding, a hysterectomy may be necessary.
Postpartum Hemorrhage and Boggy Uterus: What You Need to Know
What is Postpartum Hemorrhage?
Postpartum hemorrhage is excessive bleeding during or after childbirth. It’s a severe complication that can occur due to a boggy uterus.
Causes of Postpartum Hemorrhage
The most common cause of PPH is uterine atony, which means the uterus fails to contract after delivery. Other factors that can contribute to PPH are multiple births, prolonged labor, and the use of medications to induce or speed up labor.
Prevention and Treatment of Postpartum Hemorrhage
To prevent PPH, you should receive proper prenatal care and have a healthcare provider monitor you during labor and delivery. In the case of PPH, immediate medical attention is necessary to stop the bleeding and treat the underlying causes. Treatment options include medications, surgery, and blood transfusions.
Preventing Boggy Uterus: Tips and Strategies for Women
A boggy uterus is a condition where the uterus fails to contract effectively after delivery. This can result in excessive bleeding, which can be dangerous for the mother. While a boggy uterus can happen to anyone, there are several ways to prevent it.
Preventative Measures During Pregnancy
Regular prenatal care is the first step to prevent a boggy uterus. During prenatal visits, your healthcare provider will monitor the size and health of your uterus. They can also address any medical conditions that could affect your pregnancy, like high blood pressure or diabetes.
Healthy lifestyle habits can also help prevent a boggy uterus. Eating a nutritious diet, getting enough rest, and staying hydrated can all contribute to a healthy pregnancy.
Self-Care and Recovery Tips
If you are experiencing symptoms of a boggy uterus, it’s important to seek medical attention right away. In some cases, medication or surgery may be necessary. After delivery, you can take steps to promote uterine contraction and prevent further bleeding. This may include breastfeeding, which releases hormones that stimulate uterine contractions, and getting up and moving around as soon as possible.
Postpartum Care and Follow-Up
After delivery, it’s important to continue regular follow-up care with your healthcare provider. They can monitor your recovery and address any complications that arise. Your healthcare provider may also recommend additional treatments, like medication or uterine massage, to promote uterine contraction and prevent bleeding.
Boggy Uterus vs. Other Uterine Conditions: How to Differentiate Them
The boggy uterus is just one of several uterine conditions that can affect women. Understanding the differences between these conditions can help with diagnosis and treatment.
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that can develop in the uterus. Symptoms can include heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and frequent urination. Treatment options may include medication, surgery, or a combination of both.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it. Symptoms can include painful periods, pelvic pain, and infertility. Treatment options may include medication, surgery, or a combination of both.
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows into the uterine wall. Symptoms can include heavy menstrual bleeding, painful periods, and pelvic pain. Treatment options may include medication, surgery, or a combination of both.
Coping with the Emotional and Physical Effects of Boggy Uterus
Dealing with a uterine condition like a boggy uterus can be emotionally and physically challenging. Fortunately, there are ways to cope with these effects.
Dealing with the Physical Effects of Boggy Uterus
If you are experiencing physical symptoms of a boggy uterus, it’s important to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider can recommend treatment options to address your symptoms. In addition, self-care measures like rest, adequate hydration, and a healthy diet can help support your recovery.
Emotional Support and Coping Strategies
Dealing with a uterine condition can be stressful and emotionally challenging. It’s important to reach out for emotional support during this time. This may include talking with loved ones, joining a support group, or seeing a mental health professional.
Other coping strategies may include self-care practices like exercise, meditation, or journaling. Remember, taking care of yourself is an important part of managing a uterine condition.
In conclusion, a boggy uterus is a condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. However, with proper medical care and attention, women can reduce their risk of developing a boggy uterus and manage its symptoms effectively.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition, women can take an active role in their own health and well-being. We hope that this article has provided you with the information and resources you need to stay informed and prepared.
FAQ
What are the risk factors associated with a boggy uterus?
Women who have previously experienced postpartum hemorrhage, prolonged labor, or have delivered a large baby or twins are at an increased risk for developing a boggy uterus. Additionally, women with underlying medical conditions such as obesity, high blood pressure, or diabetes may also be at a higher risk.
What are the treatment options for a boggy uterus?
The treatment for a boggy uterus depends on its severity and underlying cause. In mild cases, medication and hormonal therapies may be used to stimulate uterine contractions and promote healing. In more severe cases, surgical intervention such as a hysterectomy or uterine artery embolization may be necessary.
Can a boggy uterus be prevented?
While not all cases of boggy uterus can be prevented, there are steps that women can take to reduce their risk. These include receiving proper prenatal care, maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine, and following their healthcare provider’s recommendations for delivery.
What should I do if I suspect I have a boggy uterus?
If you experience any symptoms of a boggy uterus such as heavy bleeding or abdominal pain, seek medical attention immediately. Your healthcare provider will be able to evaluate your symptoms and recommend the appropriate treatment options.
You May Also Like
- NVS Staff Nurse Vacancy 2024 – How to Apply
- AIIMS NORCET 6 and ESIC Nursing Exam Questions and Answers
- ESIC Nursing Officer Recruitment 2024 | 1930 Vacancies – Apply Now
- Dream Job Alert: AIIMS NORCET Nursing Officer Vacancy 2024 – Apply Now!
- NIMHANS Nursing Officer Exam 17-12-2023 Memory-Based Solved Questions