Table of Contents
Synechiae Uterus
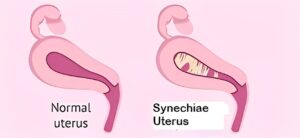
Synechiae Uterus, also known as Asherman Syndrome, is a condition that affects the uterus and can cause infertility and menstrual problems. It is characterized by scar tissue (adhesions) forming inside the uterine cavity, which can block or reduce the space for a fertilized egg to implant and grow.
What causes Synechiae Uterus?
The most common cause of Synechiae Uterus is trauma to the lining of the uterus (endometrium), usually from a surgical procedure such as dilation and curettage (D&C), which is done to remove tissue after a miscarriage, abortion, or delivery. Other causes include infections of the endometrium, such as tuberculosis, or surgery to remove fibroids or polyps from the uterus.
What are the symptoms of Synechiae Uterus?
Synechiae Uterus may not cause any symptoms until it affects fertility or menstruation. Some of the possible symptoms include:
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
- Recurrent miscarriages or pregnancy loss
- Absent or reduced menstrual flow (amenorrhea or hypomenorrhea)
- Painful or irregular periods (dysmenorrhea)
- Pelvic pain or cramps
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
How is Synechiae Uterus diagnosed?
Synechiae Uterus can be diagnosed by a gynecologist using various tests and imaging techniques, such as:
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG): A type of X-ray that uses a dye to show the shape and size of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. It can reveal any adhesions or blockages in the uterus.
- Ultrasound: A scan that uses sound waves to create images of the uterus and other pelvic organs. It can show the thickness and texture of the endometrium and any adhesions or fluid in the uterus.
- Sonohysterography: A type of ultrasound that uses a saline solution to inflate the uterine cavity and make it easier to see any adhesions or abnormalities.
- Hysteroscopy: A type of procedure that uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light (hysteroscope) to examine the inside of the uterus. It can also be used to remove adhesions or other tissue from the uterus.
How is Synechiae Uterus treated?
The main goal of treatment for Synechiae Uterus is to restore the normal function and shape of the uterine cavity and improve fertility and menstrual health. The treatment options include:
- Hysteroscopic adhesiolysis: A type of surgery that uses a hysteroscope to cut and remove adhesions from the uterus. This can improve the chances of pregnancy and reduce menstrual problems.
- Hormonal therapy: A type of medication that uses estrogen and progesterone to stimulate the growth and shedding of the endometrium. This can prevent new adhesions from forming and improve menstrual regularity.
- Intrauterine device (IUD): A type of birth control device that is inserted into the uterus and releases hormones or copper. This can prevent new adhesions from forming and reduce menstrual bleeding.
- Assisted reproductive technology (ART): A type of fertility treatment that involves using techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intrauterine insemination (IUI) to help achieve pregnancy. This can bypass any adhesions or blockages in the uterus.
What are the complications of Synechiae Uterus?
Synechiae Uterus can have a negative impact on a woman’s quality of life and emotional well-being. Some of the possible complications include:
- Chronic pelvic pain or discomfort
- Depression or anxiety
- Low self-esteem or body image
- Sexual dysfunction or reduced libido
- Relationship problems or marital stress
What are the prevention tips for Synechiae Uterus?
Synechiae Uterus cannot be prevented entirely, but some steps can be taken to reduce the risk of developing it, such as:
- Avoiding unnecessary D&C procedures or opting for less invasive alternatives
- Seeking prompt treatment for any uterine infections or inflammations
- Using antibiotics before and after any uterine surgery
- Following up with regular pelvic exams and ultrasound scans
Final Words
Synechiae Uterus is a condition that can affect a woman’s reproductive and menstrual health. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms or have a history of uterine trauma or infection. With proper diagnosis and treatment, Synechiae Uterus can be managed and overcome.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your doctor before making any changes to your health care regimen.
FAQs
Q: What is Synechiae Uterus?
A: Synechiae Uterus is a condition that causes scar tissue (adhesions) to form inside the uterine cavity, which can affect fertility and menstruation.
Q: What causes Synechiae Uterus?
A: Synechiae Uterus is usually caused by trauma to the lining of the uterus (endometrium), such as from a surgical procedure like dilation and curettage (D&C), an infection of the endometrium, or surgery to remove fibroids or polyps from the uterus.
Q: What are the symptoms of Synechiae Uterus?
A: Synechiae Uterus may not cause any symptoms until it affects fertility or menstruation. Some of the possible symptoms include infertility, recurrent miscarriages, absent or reduced menstrual flow, painful or irregular periods, pelvic pain, and abdominal bloating.
Q: How is Synechiae Uterus diagnosed?
A: Synechiae Uterus can be diagnosed by a gynecologist using various tests and imaging techniques, such as hysterosalpingogram (HSG), ultrasound, sonohysterography, or hysteroscopy.
Q: How is Synechiae Uterus treated?
A: The main goal of treatment for Synechiae Uterus is to restore the normal function and shape of the uterine cavity and improve fertility and menstrual health. The treatment options include hysteroscopic adhesiolysis, hormonal therapy, intrauterine device (IUD), or assisted reproductive technology (ART).
Q: What are the complications of Synechiae Uterus?
A: Synechiae Uterus can have a negative impact on a woman’s quality of life and emotional well-being. Some of the possible complications include chronic pelvic pain, depression, low self-esteem, sexual dysfunction, relationship problems, or marital stress.
Q: What are the prevention tips for Synechiae Uterus?
A: Synechiae Uterus cannot be prevented entirely, but some steps can be taken to reduce the risk of developing it, such as avoiding unnecessary D&C procedures, seeking prompt treatment for any uterine infections, using antibiotics before and after any uterine surgery, and following up with regular pelvic exams and ultrasound scans.