Types of Bone Fracture
Stress Fracture
A stress fracture is a small crack in a bone or severe bruising within a bone. Most stress fractures are caused by overuse and repetitive activity and are common in runners and athletes who participate in running sports, such as soccer and basketball.
Hairline fracture
A hairline fracture, also known as a stress fracture, is a small crack or severe bruise within a bone. This injury is most common in athletes, especially athletes of sports that involve running and jumping. People with osteoporosis can also develop hairline fractures.
Colles Fracture
A Colles’ fracture is a type of fracture of the distal forearm in which the broken end of the radius is bent backward. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and bruising.
Avulsion Fracture
An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture that occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma.
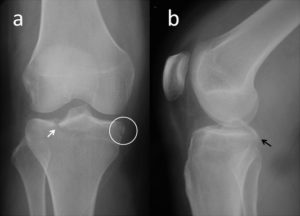
Segond Fracture
The Segond fracture is a type of avulsion fracture (soft tissue structures tearing off bits of their bony attachment) of the lateral tibial condyle of the knee, immediately beyond the surface which articulates with the femur.
Comminuted Fracture
A comminuted fracture is a break or splinter of the bone into more than two fragments. Since considerable force and energy is required to fragment bone, fractures of this degree occur after high-impact trauma such as in vehicular accidents
Greenstick fracture
A greenstick fracture is a fracture in a young, soft bone in which the bone bends and breaks. Greenstick fractures occur most often during infancy and childhood when bones are soft. The name is by analogy with green (i.e., fresh) wood which similarly breaks on the outside when bent.
Compound Fracture
An open fracture also called a compound fracture, is a fracture in which there is an open wound or break in the skin near the site of the broken bone. Most often, this wound is caused by a fragment of bone breaking through the skin at the moment of the injury.
Compression Fracture
A compression fracture is typically caused by a loss of bone mass (osteoporosis) that occurs as part of aging. A fall, a cough or lifting a heavy object may cause a fracture of the backbones.
Buckle fracture or Torus Fracture
A buckle fracture is sometimes referred to as an “incomplete fracture,” because the break is only on one side of the long bone of the arm or leg. This injury is also called a “torus fracture,” and is most common in children whose bones are softer and less brittle than adults.
Jones Fracture
A Jones fracture is a break between the base and middle part of the fifth metatarsal of the foot. It results in pain near the midportion of the foot on the outside.
Salter-Harris Fracture
A Salter-Harris fracture is a fracture that involves the epiphyseal plate or growth plate of a bone, specifically the zone of provisional calcification. It is thus a form of child bone fracture.
Tillaux fracture
Tillaux fractures are Salter-Harris III fractures through the anterolateral aspect of the distal tibial epiphysis, with variable amounts of displacement.
Monteggia Fracture
The Monteggia fracture is a fracture of the proximal third of the ulna with dislocation of the proximal head of the radius. It is named after Giovanni Battista Monteggia
Galeazzi Fracture
The Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the distal third of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint.
Lisfranc Fracture or Lisfranc injury
Lisfranc injury, also known as Lisfranc fracture, is an injury of the foot in which one or more of the metatarsal bones are displaced from the tarsus.
Le fort fracture
Le Fort fractures are fractures of the midface, which collectively involve separation of all or a portion of the midface from the skull base. In order to be separated from the skull base, the pterygoid plates of the sphenoid bone need to be involved as these connect the midface to the sphenoid bone dorsally.
Basal Skull fracture
A basilar skull fracture is a break of a bone in the base of the skull. Symptoms may include bruising behind the ears, bruising around the eyes, or blood behind the eardrum. A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak occurs in about 20% of cases and can result in fluid leaking from the nose or ear
Smith Fracture
A Smith’s fracture, is a fracture of the distal radius. It is caused by a direct blow to the dorsal forearm or falling onto flexed wrists, as opposed to a Colles’ fracture which occurs as a result of falling onto wrists in extension.
Bennett Fracture
Bennett fracture is a fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone which extends into the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint. This intra-articular fracture is the most common type of fracture of the thumb and is nearly always accompanied by some degree of subluxation or frank dislocation of the carpometacarpal joint.
Impacted Fracture
An impacted fracture occurs when the broken ends of the bone are jammed together by the force of the injury. A comminuted fracture is one in which the broken ends of the bone are shattered into many pieces.
Chance Fracture
A Chance fracture is a type of vertebral fracture that results from excessive flexion of the spine. Symptoms may include abdominal bruising (seat belt sign), or less commonly paralysis of the legs
Burst Fracture
A burst fracture is a type of traumatic spinal injury in which a vertebra breaks from a high-energy axial load (e.g., traffic collisions or falls from a great height or high speed, and some kinds of seizures, or jumping into a swimming pool at the shallow end whilst intoxicated), with shards of vertebra penetrating surrounding tissues and sometimes the spinal canal
Occult fracture
An occult fracture is one that does not appear well on an X-ray. A possible occult fracture is a suspected fracture that needs to be confirmed with other imaging tests. Occult fractures can occur because of a fall or other type of sudden (acute) injury.
Toddler fracture
A toddler’s fracture is a spiral or oblique undisplaced fracture of the distal shaft of the tibia with an intact fibula. The periosteum remains intact and the bone is stable. These fractures occur as a result of a twisting injury. Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis should be excluded.
Tuft fracture
Tuft fractures the mechanism is usually crushing injury. usually stable due to the nail plate dorsally and pulp volar, often associated with laceration of nail matrix or pulp
Tripod fracture
The zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture, also known as a quadripod fracture, quadramalar fracture, and formerly referred to as a tripod fracture or trimalar fracture, has four components: the lateral orbital wall (at either the zygomaticofrontal suture superiorly along the wall or zygomaticosphenoid suture inferiorly), separation of the maxilla and zygoma along the anterior maxilla (near the zygomaticomaxillary suture), the zygomatic arch, and the orbital floor near the infraorbital canal.
Boxers fracture
A boxer’s fracture is the break of the 5th metacarpal bones of the hand near the knuckle. Occasionally it is used to refer to fractures of the 4th metacarpal as well. Symptoms include pain and a depressed knuckle. Classically, it occurs after a person hits an object with a closed fist
Types Of Fracture- Mostly Asked Nursing Quiz
-
Open reduction and internal fixation
-
Carpal tunnel release
-
Arthroplasty
-
Knee replacement
The Correct answer is Carpal tunnel release
Q2) What is the other name of necrotizing fasciitis?
-
Flesh-eating disease
-
Psoriasis
-
Seborrhea
-
Cellulitis
The Correct answer is flesh-eating diseasse
Q3) In which bone the Hangman’s fracture occurs?
-
The distal end of the radius
-
The distal part of the fibula
-
Pedicle of C-2 cervical vertebrae
-
Neck of femur
The correct answer is pedicle of C – 2 cervical vertebrae
Q4) What is known as a fracture with bending and splintering?
-
Complete fracture
-
Comminuted fracture
-
Greenstick fracture
-
Pott’s fracture
The correct answer is comminuted fracture
-
Periosteum
-
Epiphysis
-
Diaphysis
-
Medullary Cavity
The correct answer is periosteum
-
Comminuted fracture
-
Pathological fracture
-
Oblique fracture
-
Stress fracture
The correct answer is stress fracture
-
Compound fracture
-
Colle’s fracture
-
Pathological fracture
-
Greenstick fracture
The correct answer is pathological fracture
-
Ganglion cyst
-
Chondromalacia
-
Fibromyalgia
-
Bursitis
The correct answer is Fibromyalgia
-
Vascular injury.
-
Nerve injury
-
Compartment syndrome.
The correct answer is stroke
Q10) Which one of the following is one purpose of traction?
-
Increase the muscle spasm
-
Reduce the infection
-
Immobilize the fractured part
-
All of the above
The correct answer is immoblize the fractured part
Q11) The following things affect bone healing after fracture except …….?
-
Age of the person
-
Underlying bone pathology
-
Bone type
-
Arthroscopy
The correct answer is arthroscopy
Please Subscribe Our YouTube channel – The Nurse
Like our Facebook Page: The Nurse
Please Subscribe to get all our posts in your mail inbox