Table of Contents
Novel Corona Virus (2019-nCoV) – COVID – 19
According to WHO, On 31 December 2019, WHO was cautioned to a few instances of pneumonia in Wuhan City, Hubei Province of China. The infection didn’t coordinate some other known infection. This raised concern since when an infection is new, we don’t have the foggiest idea of how it affects individuals.
One week later, on 7 January, Chinese specialists affirmed that they had distinguished another infection. The new infection is a coronavirus, which is a group of infections that incorporate the common cold, and viruses such as, SARS and MERS. This new infection was briefly named “2019-nCoV.” Now it is known as COVID – 19
On 11 February 2020, WHO announced a name for the new coronavirus disease – COVID – 19
WHO has been working with Chinese specialists and worldwide specialists from the day we were informed, to study the infection, how it influences the individuals who are debilitated with it, how they can be dealt with, and what nations can do to react.
Since this is a coronavirus, which for the most part causes respiratory sickness, WHO has prompted individuals on the best way to shield themselves and people around them from getting the illness.
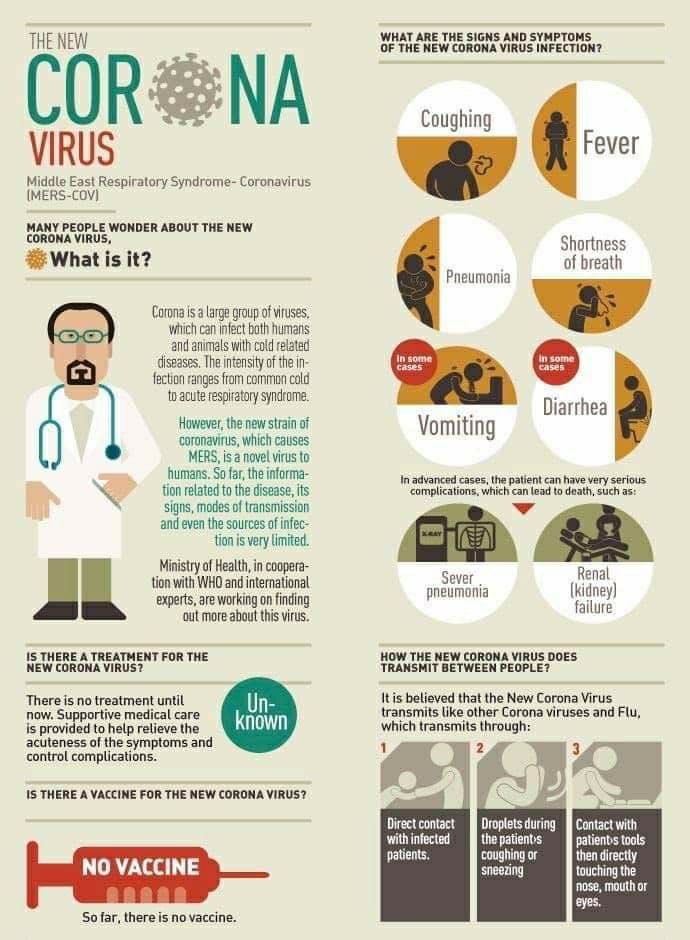
What is Coronavirus?
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that cause illness in humans and animals. Coronaviruses are the largest RNA viruses. “Corona” refers to the prominent halo or club-shaped in the envelope.
In people, coronaviruses can cause illnesses ranging in severity from the common cold to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome caused by (SARS CoV).
This second coronavirus strain is known as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS CoV). New China strains SARS-like virus is termed as COVID – 19
What are the symptoms of Coronavirus / COVID – 19 infection in humans?
- Fever
- Cough
- Breathing difficulties
- Most patients have had pneumonia
- In some cases: Diarrhea
- In Advanced Cases: Respiratory failure
- Symptoms may last about a week with considerable variation between patients
Incubation Period: 10 – 14 Days
Laboratory Diagnosis
Antigen and Nucleic Acid detection
Coronavirus antigens in cells in respiratory secretions may be detected using the ELISA test if a high-quality antiserum is available
Enteric coronaviruses can be detected by examination of stool samples by Electron microscopy
Coronaviruses RNA was detectable in plasma by PCR, with viremia most readily detectable between days 4 and 8 of infection

How coronavirus/COVID – 19 is transmitted?
- Mingling with affected people
- Droplets from coughs or sneezes
- Germs are often spread when a person touches something that is contaminated with germs and then touches his or her eyes, nose or mouth

Is there a vaccine for coronavirus?
No, there is no vaccine available now
What is the treatment for coronavirus?
There is no definite treatment for coronavirus infection but can reduce the acute illness symptoms and complications with early treatment. The treatment focused on supportive therapy and should be based on a patient’s clinical condition. The treatment with Hydroxychloroquine, convalescent plasma transfusion, antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV/AIDS are going on under trial experiments.
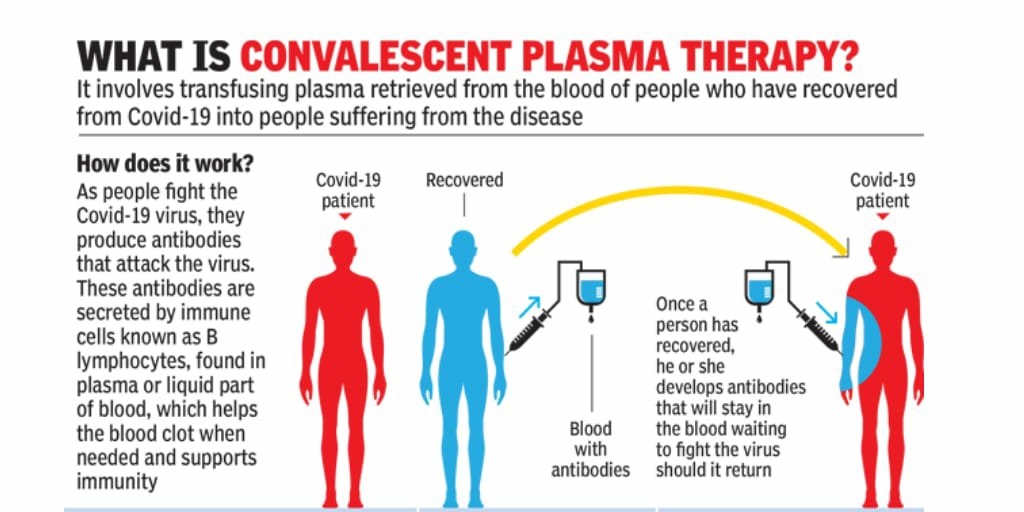
Convalescent Plasma Therapy
Convalescent Plasma Therapy is a classic adaptive immunotherapy. It has been used in prevention and cure of infectious disease for over a century
It was successfully used in treatment for SARS, MERS and 2009 H1N1 Pandemic, and found to be effective and safe.
In this therapy, blood plasma from a person who has recovered from the same infection is taken. It is then transfused into an infected and seriously ill person suffering from the same infection – in this case covid 19
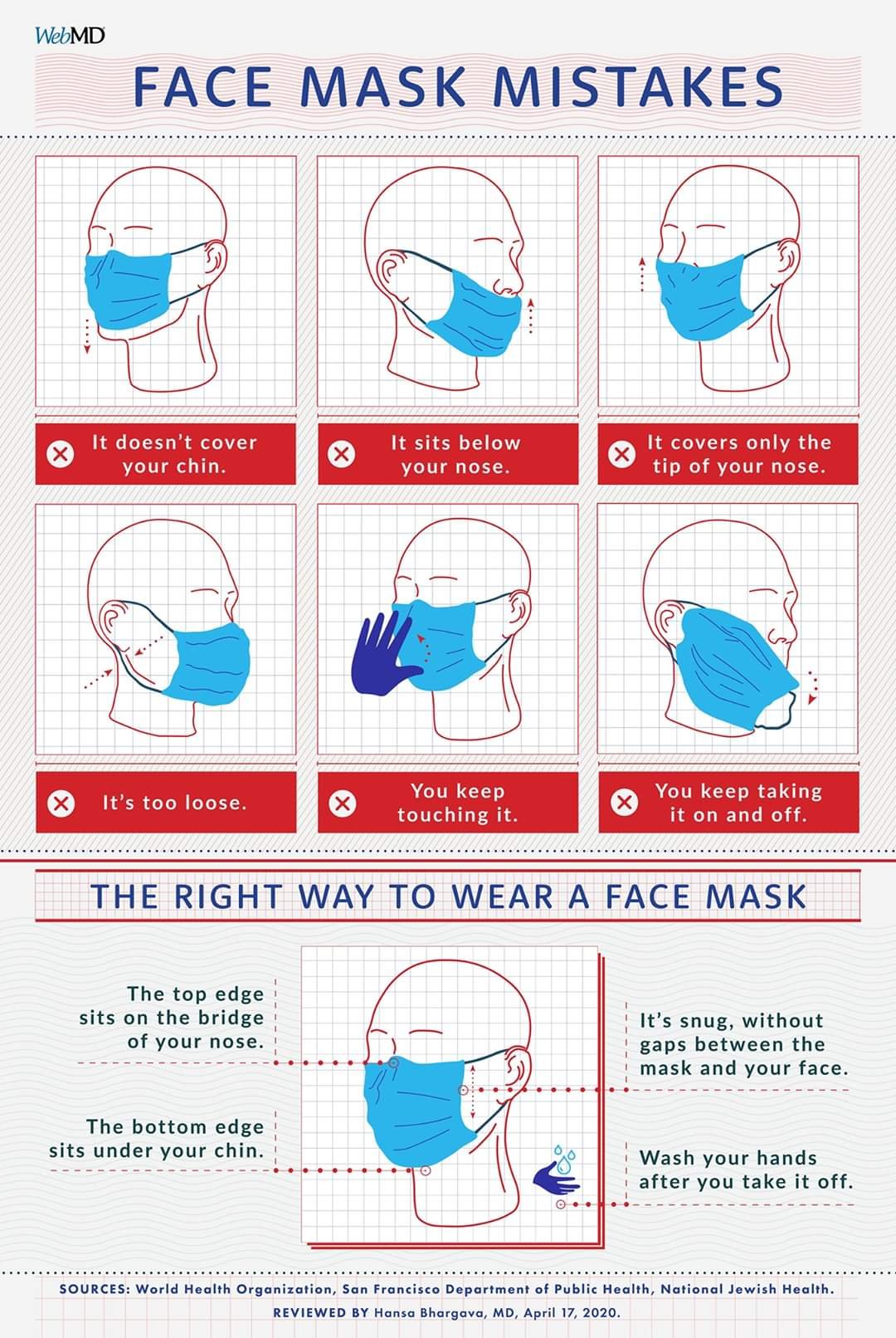
How to Protect Yourself from COVID – 19?
First and foremost thing is handwashing, So wash your hands
- After coughing or sneezing
- When caring for the sick
- Before, during and after you prepare food
- Before eating
- After the toilet use
- When hands are visibly dirty
- After handling animals or animal waste
How to Make Home Isolation for Protecting From Covid-19 Infection
No visitors unless the person needs to be in your home.
—If you need medical attention, call ahead to ensure you’re going to the right place and taking the necessary precautions.
—Wear a face mask if you must be around other people, such as during a drive to the doctor’s office.
—When you cough/sneeze:
Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue; immediately throw tissues in the garbage; wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds; if that’s not available, clean with hand sanitizer that has at least 60% alcohol (here’s how to make your own hand sanitizer).
—Avoid sharing household items, including drinking cups, eating utensils, towels or even bedding. Wash these items thoroughly after using them.
—Clean high-touch surfaces daily using a household cleaner or wipe. These include: “counters, tabletops, doorknobs, bathroom fixtures, toilets, phones, keyboards, tablets, and bedside tables,” the CDC says.
—Clean any surfaces that may be contaminated with blood, stool or any bodily fluids.
—Shared spaces in the home should have good airflow — use an air conditioner or open windows.
—Continue monitoring your symptoms. If they worsen, such as you if you begin to have difficulty breathing, call your health care provider.
When to stop isolating?
To figure out when to stop your isolation measures, the CDC says this will be on a case-by-case basis, so you should check with your health care provider before making any changes.
Advisory of Social Distancing By Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt. Of India
Advisory on Social Distancing Measure in view of spread of COVID-19 disease
Social distancing is a non-pharmaceutical infection prevention and control intervention implemented to avoid/decrease contact between those who are infected with a disease-causing pathogen and those who are not, so as to stop or slow down the rate and extent of disease transmission in a community.
This eventually leads to a decrease in spread, morbidity, and
mortality due to the disease. In addition to the proposed interventions, the State/UT Governments may prescribe such other measures as they consider necessary.
All these proposed interventions shall be in force till the 31st of March, 2020. They will be reviewed as per the evolving situation.
The following interventions are proposed:
- Closure of all educational establishments (schools, universities etc), gyms, museums,
cultural and social centres, swimming pools and theatres. Students should be advised
to stay at home. Online education to be promoted. - Possibility of postponing exams may be explored. Ongoing exams to be conducted only
after ensuring physical distance of one meter amongst students. - Encourage private sector organizations/employers to allow employees to work from
home wherever feasible. - Meetings, as far as feasible, shall be done through video conferences. Minimize or
reschedule meetings involving large number of people unless necessary. - Restaurants to ensure handwashing protocol and proper cleanliness of frequently
touched surfaces. Ensure physical distancing (minimum 1metre) between tables;
encourage open air seating where practical with adequate distancing. - Keep already planned weddings to a limited gathering, postpone all non-essential social
and cultural gatherings. - Local authorities to have a dialogue with organizers of sporting events and competitions
involving large gatherings and they may be advised to postpone such events. - Local authorities to have a dialogue with opinion leaders and religious leaders to
regulate mass gatherings and should ensure no overcrowdin g/at least one metre distance
between people. - Local authorities to have meeting with traders associations and other stakeholders t oregulate hours, exhibit Do’s and Don’ts and take up a communication drive in market places like sabzi mandi, anaj mandi, bus depots, railway stations, post-offices etc., where essential services are provided.
- All commercial activities must keep a distance of one meter between customers. Measures to reduce peak hour crowding in markets.
- Non-essential travel should be avoided. Buses, Trains and aeroplanes to maximize social distancing in public transport besides ensuring regular and proper disinfection of surfaces.
- Hospitals to follow necessary protocol related with COVID-19 management as prescribed and restrict family/friends/children visiting patients in hospitals.
- Hygiene and physical distancing has to be maintained. Shaking hands and hugging as a matter of greeting to be avoided.
- Special protective measures for delivery men/ women working in online ordering services.
- Keep communities informed consistently and constantly.
Anatomy and Pathophysiology Multiple choices Questions